
(b) How far the car has travelled when it reaches a velocity of 30 m/s. If the initial velocity of the car is 5 m/s, determine: This then helps in the choice of which equation(s) to use for the solution.Įxample 7: A car has an acceleration of 3m/s². When solving problems in kinematics it is often useful if the given information is written down in terms of a, u, v, t and s. Even if the average speed of answer seems reasonable, it will need to be improved if there are still high customer abandonment rates. To make up for this blind spot, be sure to look at customer abandonment rates as well. In practice, s can often be used to denote distance because if the direction of motion does not change then the displacement and distance travelled are equal. Average speed of answer in isolation doesn’t give any information about the impact of the time frame necessary for a response. Strictly speaking s represents displacement in the above formulae. The above four equations are used to solve problems involving uniform acceleration in kinematics.
Substitute for t = (v - u)/a in (ii) gives: Various equations of motion can be derived as follows:Īcceleration = increase in velocity/time takenĪverage velocity = (u + v)/2 because the acceleration is uniform. Retardation is the reverse of acceleration and therefore can be written as negative acceleration.Įxample 1: The velocity of a body decreases from 25 m/s to 5 m/s in 4 s. It is represented by the equation: vrms 3RT M v r m s 3 R T M, where v rms is the root-mean-square of the velocity, M m is the molar mass of the gas in kilograms per mole, R. Retardation is the term that is usually used. The root-mean-square speed is the measure of the speed of particles in a gas, defined as the square root of the average velocity-squared of the molecules in a gas. Note that the units of acceleration m/s² are obtained by dividing m/s by s.īodies also slow down and this is called deceleration or retardation. constant for a given set of circumstances.Įxample 5: The velocity of a body increases from 2 m/s to 18 m/s in 8 s.

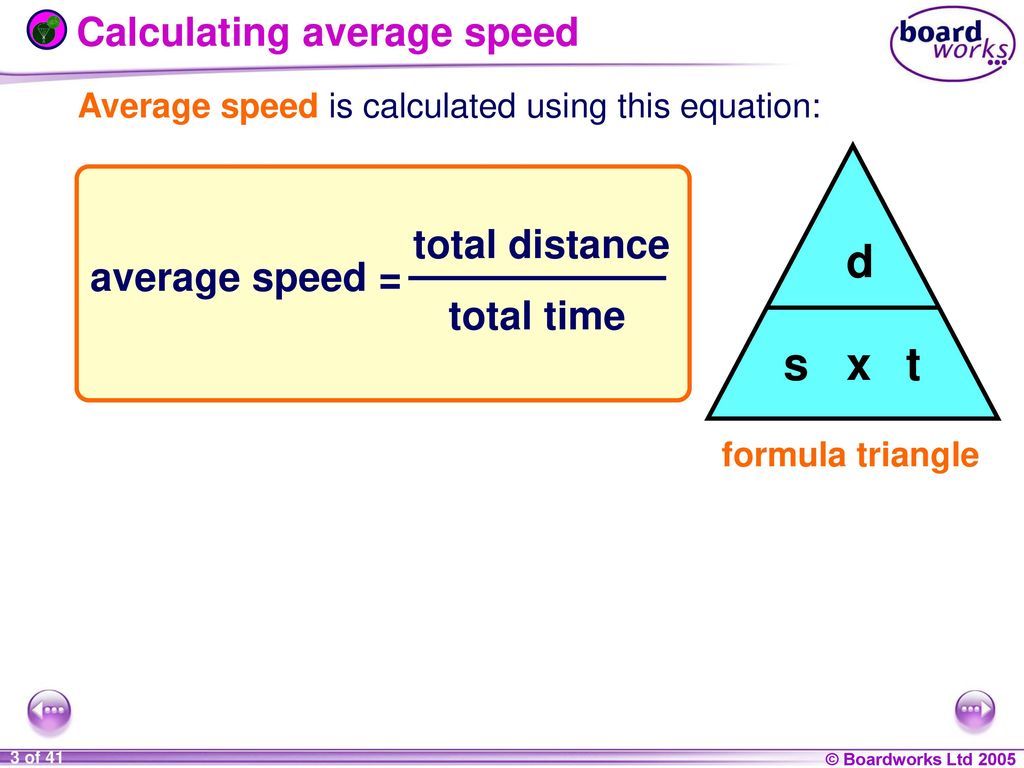
Equations of motion involving acceleration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
